Rigging: The System of Ropes, Wires, and Other Components that Support and Control the Sails on a Sailboat
Definition: Rigging refers to the system of ropes, wires, and other hardware used on a sailboat to support the mast and control the sails. This intricate network is essential for managing the boat’s sails, adjusting their angle to the wind, and ensuring the structural integrity of the mast and spars.
Understanding Rigging:
Rigging is divided into two main categories: standing rigging and running rigging. Each plays a crucial role in the overall performance and safety of a sailboat.
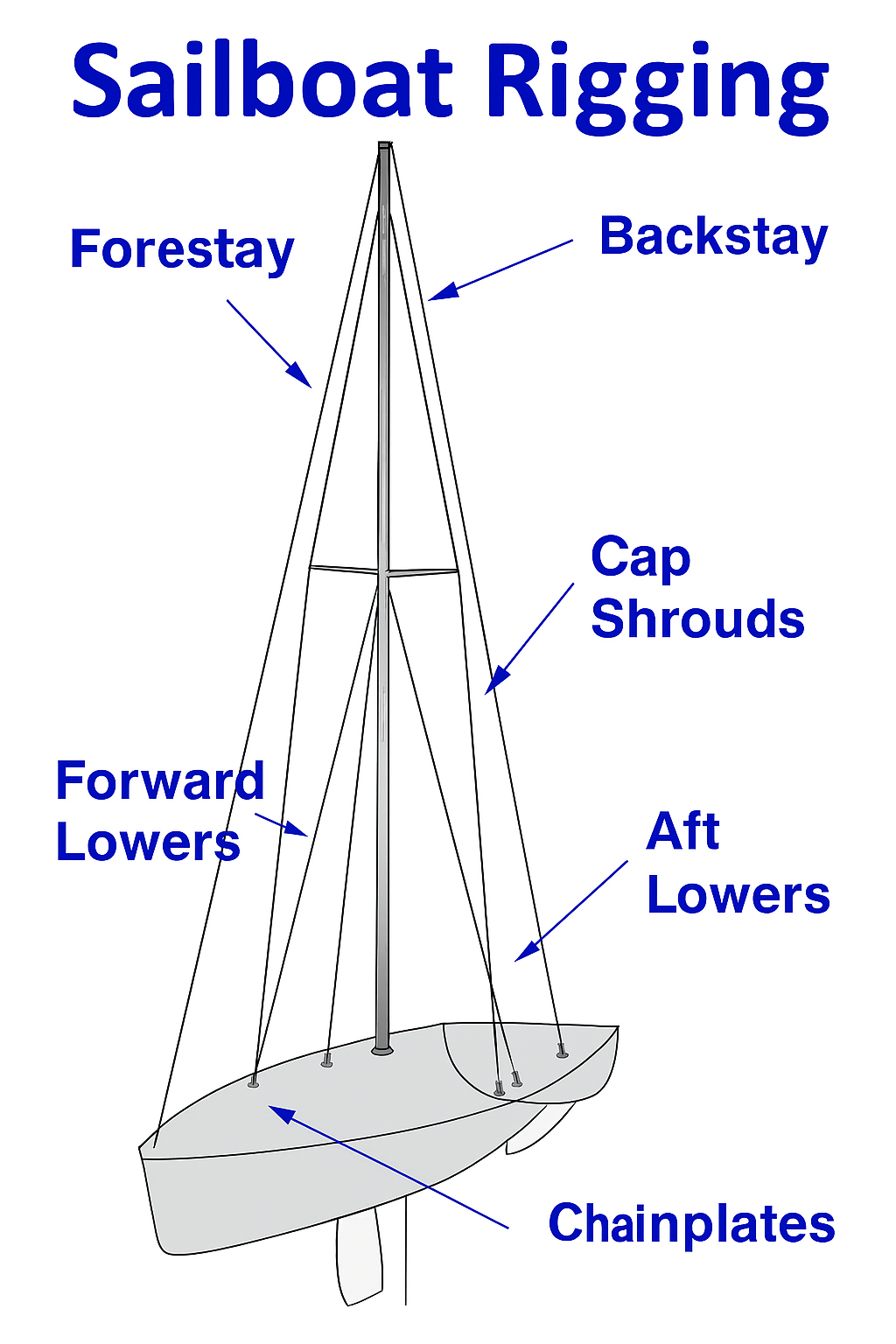
Standing Rigging: Comprises the fixed lines, wires, and rods that support the mast and keep it upright. This includes shrouds, stays (forestay and backstay), and spreaders. The standing rigging is typically made of strong, durable materials like stainless steel wire or rod, designed to withstand the constant stress and tension of holding the mast in place.
Running Rigging: Refers to the movable lines and ropes used to control the sails, such as halyards, sheets, and control lines. These components are adjusted frequently during sailing to raise, lower, and trim the sails according to wind conditions and desired boat speed.
Components of Rigging:
Shrouds: Wires that run from the mast to the sides of the boat, providing lateral support.
Stays: Wires or rods that run from the mast to the bow (forestay) and stern (backstay), providing forward and aft support.
Halyards: Ropes or wires used to hoist and lower the sails.
Sheets: Ropes used to control the angle of the sails relative to the wind.
Blocks: Pulleys that help guide and adjust the running rigging, reducing friction and making it easier to control the sails.
Applications in Sailing:
Mast Support: The standing rigging ensures that the mast remains upright and stable, even under the pressure of strong winds and large sails.
Sail Control: The running rigging allows sailors to adjust the sails for optimal performance, whether they are sailing upwind, downwind, or on a reach.
Safety: Properly maintained rigging is crucial for the safety of the boat and crew, preventing mast failure and ensuring that the sails can be controlled in all conditions.
Examples of Usage:
"Inspect the rigging before each voyage to ensure all components are secure and in good condition."
"The running rigging allows us to adjust the sails quickly as the wind shifts."
"A failure in the standing rigging could lead to a dismasting, so regular maintenance is essential."
Visual Representation:
Image Description: Diagram of a sailboat showing the rigging system, with labels for standing rigging components like shrouds and stays, and running rigging components like halyards and sheets.
Importance in Sailing: Rigging is the backbone of a sailboat’s ability to sail effectively and safely. Without a well-maintained rigging system, a sailboat would be unable to properly support its mast or control its sails, leading to potential accidents or loss of performance. Regular inspection, maintenance, and understanding of the rigging system are vital for any sailor.
Related Terms:
Mast: The vertical pole that supports the sails and rigging.
Boom: The horizontal spar that holds the foot of the mainsail and is part of the running rigging system.
Halyard: A line used to hoist or lower the sails.
Sheet: A line used to control the angle of the sail relative to the wind.
Conclusion: Rigging is an essential system on a sailboat, composed of various ropes, wires, and hardware that work together to support the mast and control the sails. Understanding and maintaining the rigging is crucial for safe and efficient sailing. Whether you are preparing for a race or a leisurely cruise, a well-rigged boat is key to a successful journey on the water.